Each drive stage in Maul features 32 different algorithms with which to process the incoming signal, selected with the Drive Type drop-down menu described in the previous section.
About the graphs The graphs in this section represent the waveshaping response of most of Maul's algorithms. These do not make sense in the context of which some algorithms work, such as the Ring Mod and Digital algorithms. The x-axis of each graph represents time, while the y-axis represents amplitude. With no processing applied (with the Drive Type set to 'Thru'), the waveshaping response can be represented by the graph to the right.
DCAM |
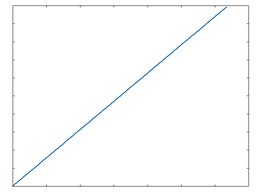 Thru |
This category contains DCAM analogue modelled distortion algorithms of diode, transistor and tube-based circuits. The following graphs show the waveshaping response at 50% and 100% Drive amounts. The x-axis represents time while the y-axis represents amplitude.
GE Diode (Germanium Diode)
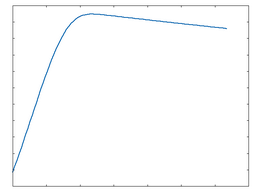 GE Diode: 50% Drive |
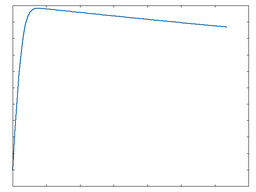 GE Diode: 100% Drive |
HR Diode (Half-Rectified Diode)
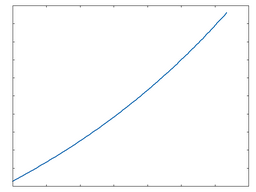 HR Diode: 50% Drive |
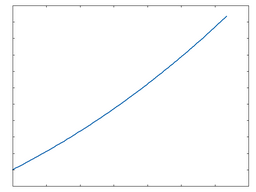 HR Diode: 100% Drive |
Op-Amp
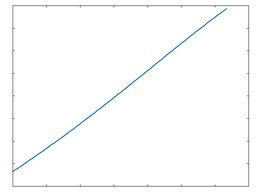 Op-Amp: 50% Drive |
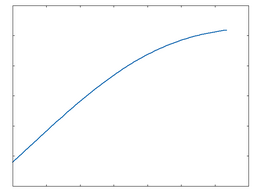 Op-Amp: 100% Drive |
JFET (Junction gate Field-Effect Transistor)
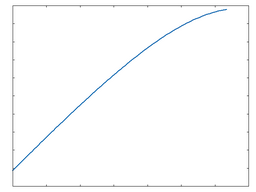 JFET: 50% Drive |
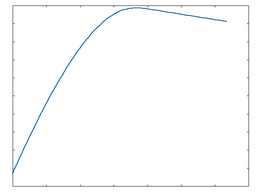 JFET: 100% Drive |
Transistor
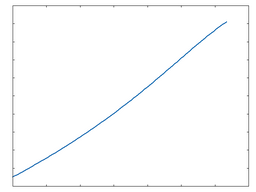 Transistor: 50% Drive |
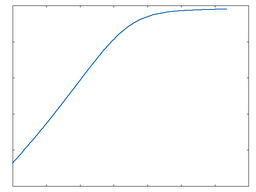 Transistor: 100% Drive |
OTA (Operational Transconductance Amplifier)
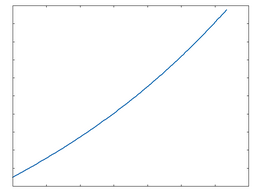 OTA: 50% Drive |
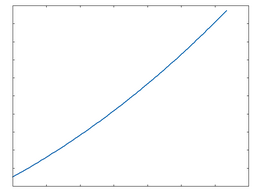 OTA: 100% Drive |
Tube
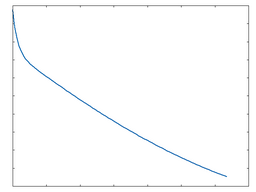 Tube: 50% Drive |
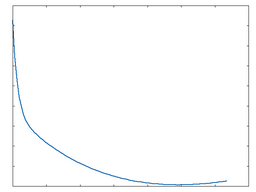 Tube: 100% Drive |
Distort
The algorithms in this category introduce inharmonic distortion. The graphs shown represent the frequency response at 50% and 100% drive amounts. TheThe following graphs show the waveshaping response at 50% and 100% Drive amounts. The x-axis represents time while the y-axis represents amplitude.
Diff
This waveshaping function outputs the difference between the incoming audio and a sine-like waveshape.
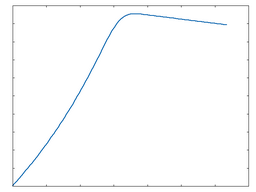 Diff: 50% Drive |
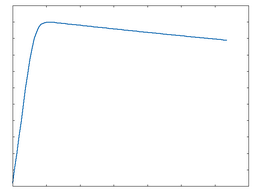 Diff: 100% Drive |
Half rect
This algorithm is a half-rectified distortion function.
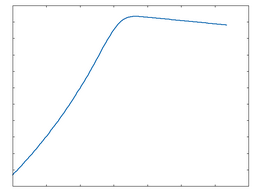 Half rect: 50% Drive |
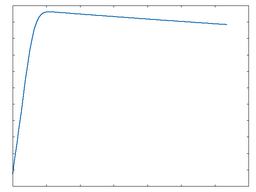 Half rect: 100% Drive |
Tri
This algorithm applies a triangle waveshaping function to the incoming audio.
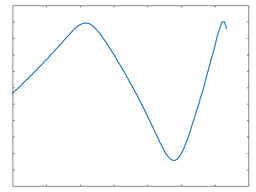 Tri: 50% Drive |
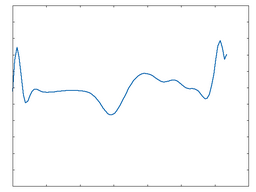 Tri: 100% Drive |
Ring Mod
These algorithms perform ring modulation of the input signal with a variety of internal carrier waveforms.
RM Sin
Ring modulator with sine wave carrier
RM Tri
Ring modulator with triangle wave carrier
RM Saw
Ring modulator with saw wave carrier
RM Square
Ring modulator with square wave carrier
RM White
Ring modulator with white noise carrier
RM Pink
Ring modulator with pink noise carrier
Overdrive
The Overdrive algorithms impart harmonic distortion upon the signal. The following graphs show the waveshaping response at 50% and 100% Drive amounts. The x-axis represents time while the y-axis represents amplitude.
Asym
This algorithm provides an asymmetrical overdrive function.
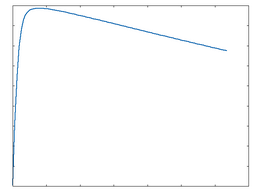 Asym: 50% Drive |
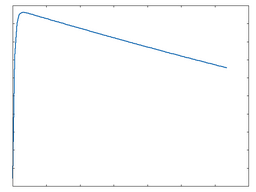 Asym: 100% Drive |
Soft
This algorithm provides a soft overdrive function.
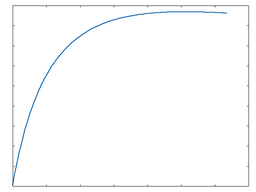 Soft: 50% Drive |
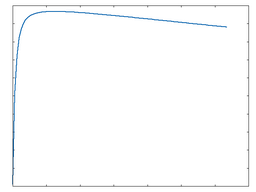 Soft: 100% Drive |
Shredder
This algorithm imparts very heavy overdrive to the signal.
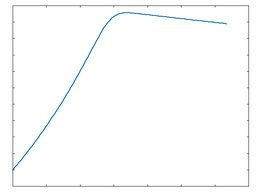 Shredder: 50% Drive |
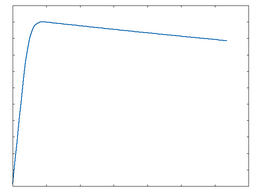 Shredder: 100% Drive |
Tannin
This algorithm is essentially a shaper based on a polynomial mathematical function, with added DC shift.
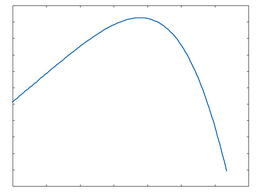 Tannin: 50% Drive |
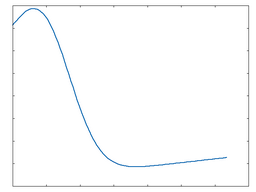 Tannin: 100% Drive |
Clipper
These algorithms DC-shift and clip the signal for a hard, abrasive type of distortion. The following graphs show the waveshaping response at 50% and 100% Drive amounts. The x-axis represents time while the y-axis represents amplitude.
Clip
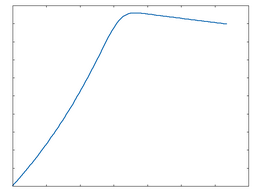 Clip: 50% Drive |
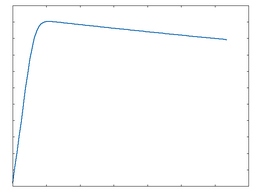 Clip: 100% Drive |
Clip Hard
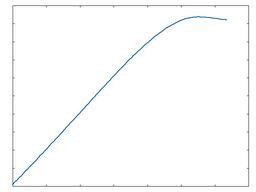 Clip Hard: 50% Drive |
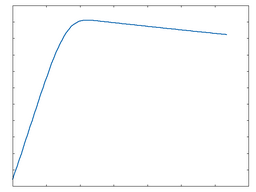 Clip Hard: 100% Drive |
Clip Rect
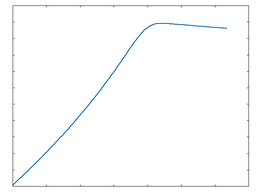 Clip Rect: 50% Drive |
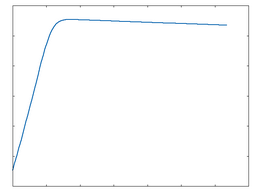 Clip Rect: 100% Drive |
Clip Half Rect
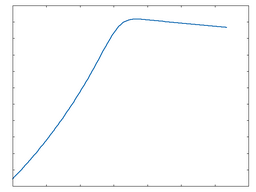 Clip Half Rect: 50% Drive |
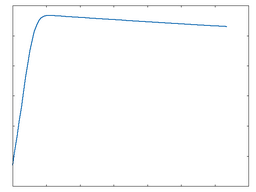 Clip Half Rect: 100% Drive |
Clip Quad Rect
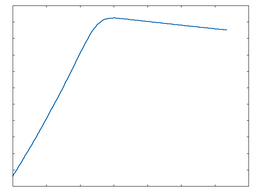 Clip Quad Rect: 50% Drive |
 Clip Quad Rect: 100% Drive |
Clip Full Rect
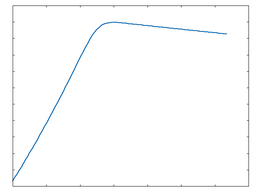 Clip Full Rect: 50% Drive |
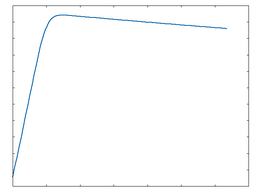 Clip Full Rect: 100% Drive |
Shaper
These algorithms apply various types of polynomial mathematical waveshaping functions to the audio signal. The following graphs show the waveshaping response at 50% and 100% Drive amounts. The x-axis represents time while the y-axis represents amplitude.
Poly 1
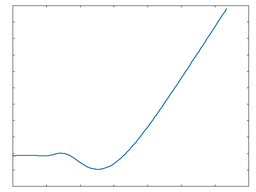 Poly 1: 50% Drive |
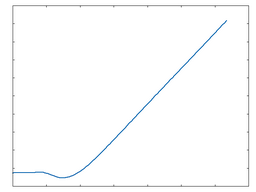 Poly 1: 100% Drive |
Poly 2
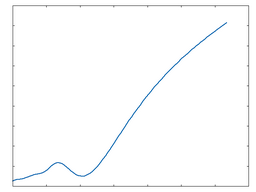 Poly 2: 50% Drive |
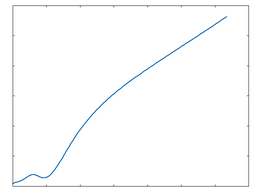 Poly 2: 100% Drive |
Poly 3
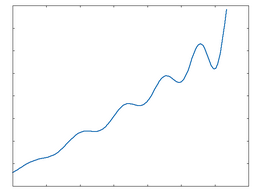 Poly 3: 50% Drive |
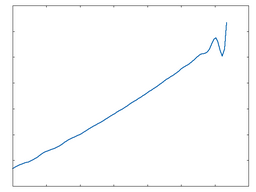 Poly 3: 100% Drive |
Poly 4
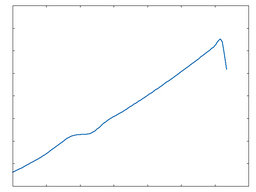 Poly 4: 50% Drive |
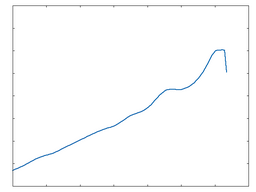 Poly 4: 100% Drive |
Digital
These algorithms simulate digital distortion caused by reducing the sample-rate and bit-depth of the signal.
Bit Reduce
This algorithm reduces the bit depth of the signal.
SR Reduce
This algorithm reduces the sample-rate of the signal, causing aliasing effects.